Neuroanatomy is a foundational subject for medical students, playing a crucial role in understanding the structure and function of the nervous system. It is a complex area of study that can be challenging to grasp, especially considering the vast number of structures and pathways involved. However, with the right approach and resources, students can efficiently learn and retain this vital knowledge.
The purpose of this article is to provide a step-by-step guide for medical students seeking to master neuroanatomy. We will discuss the optimal sequence to study the subject, share efficient study techniques, explore the use of mnemonics and mind maps, and recommend the best resources for learning. By following the guidance provided in this article, medical students can create a solid foundation in neuroanatomy and achieve their end goal of not only understanding the material but also retaining it for future application in their medical careers.
1. Establishing the Right Sequence to Study Neuroanatomy
Learning neuroanatomy in a logical and organized sequence is crucial for building a strong foundation. By following a structured approach, students can better understand and retain the material. Here is a recommended sequence for studying neuroanatomy:
1.1. Basic Terminology and Neuroanatomical Orientation
Begin by familiarizing yourself with essential neuroanatomical terms and concepts, including anatomical directions (e.g., superior, inferior, anterior, posterior) and planes of section (e.g., sagittal, coronal, axial). This foundation will help you navigate the complex structures and systems within neuroanatomy.
1.2. Overview of the Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Gain a general understanding of the two main components of the nervous system, the CNS and PNS. Learn about their respective roles, divisions, and how they interact with each other.
1.3. Gross Anatomy of the Brain
Study the brain's gross anatomy, including its major divisions (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and the key structures within each division (e.g., lobes, thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.).
1.4. Cranial Nerves
Learn about the 12 cranial nerves, their functions, and their anatomical relationships to the brain and surrounding structures.
1.5. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
Examine the anatomy and organization of the spinal cord, as well as the spinal nerves that emerge from it.
1.6. Major Pathways and Systems
Explore the significant pathways and systems within the nervous system, such as the motor and sensory pathways, and learn about their functional roles.
1.7. Functional Anatomy: Motor, Sensory, and Cognitive Systems
Delve into the functional anatomy of the nervous system by studying various motor, sensory, and cognitive systems. Understand how different brain regions contribute to specific functions, such as movement, sensation, and cognition.
1.8. Clinical Applications
Finally, apply your knowledge of neuroanatomy to clinical scenarios. Learn about common neurological disorders, their underlying anatomical and physiological causes, and their clinical manifestations. This will help you appreciate the importance of neuroanatomy in diagnosing and treating patients.
2. Efficient Study Techniques for Neuroanatomy
To optimize your neuroanatomy learning, employ the following efficient study techniques:

2.1. Active Learning Strategies
Engage with the material through active learning techniques such as summarizing, teaching others, and asking questions. These methods promote better understanding and retention compared to passive learning, like simply reading or listening to lectures.
2.2. Repetition and Spaced Repetition
Reinforce your learning by revisiting the material multiple times. Implement spaced repetition by scheduling review sessions at increasing intervals, which has been proven to enhance long-term retention.
2.3. Focused Study Sessions
Avoid multitasking and minimize distractions during study sessions. Set specific goals for each session and allocate dedicated time to focus solely on neuroanatomy.
2.4. The Pomodoro Technique
Use the Pomodoro Technique, a time-management method that breaks study sessions into focused intervals (usually 25 minutes) followed by short breaks. This can improve concentration and productivity while reducing mental fatigue.
2.5. Testing Yourself Regularly
Assess your knowledge by taking practice quizzes and tests, which will help identify areas that need improvement and reinforce your learning through retrieval practice.
3. Mnemonics and Memory Aids
Mnemonics play a crucial role in mastering neuroanatomy, as they help simplify complex information and make it more memorable.

3.1. Importance of Mnemonics in Neuroanatomy
Given the sheer volume of structures and connections in neuroanatomy, mnemonics provide a valuable tool for organizing and recalling information. They can help you remember the names, order, and functions of various structures more efficiently.
3.2. Popular Mnemonic Sources and Examples
Several resources offer neuroanatomy mnemonics, such as medical textbooks, websites, and forums. Some examples of popular mnemonics include:
- For cranial nerves: "Oh, Oh, Oh, To Touch And Feel Very Green Vegetables, AH!"
- For the spinal nerve functions: "Some Say Marry Money, But My Brother Says Big Brains Matter Most."
3.3. Creating Your Own Mnemonics
Develop your mnemonics by using familiar or personally meaningful phrases, images, or associations. This can make the information even more memorable and increase the chances of long-term retention.
4. Mind Maps for Neuroanatomy
Mind maps offer a valuable tool for visualizing and organizing complex information in neuroanatomy.
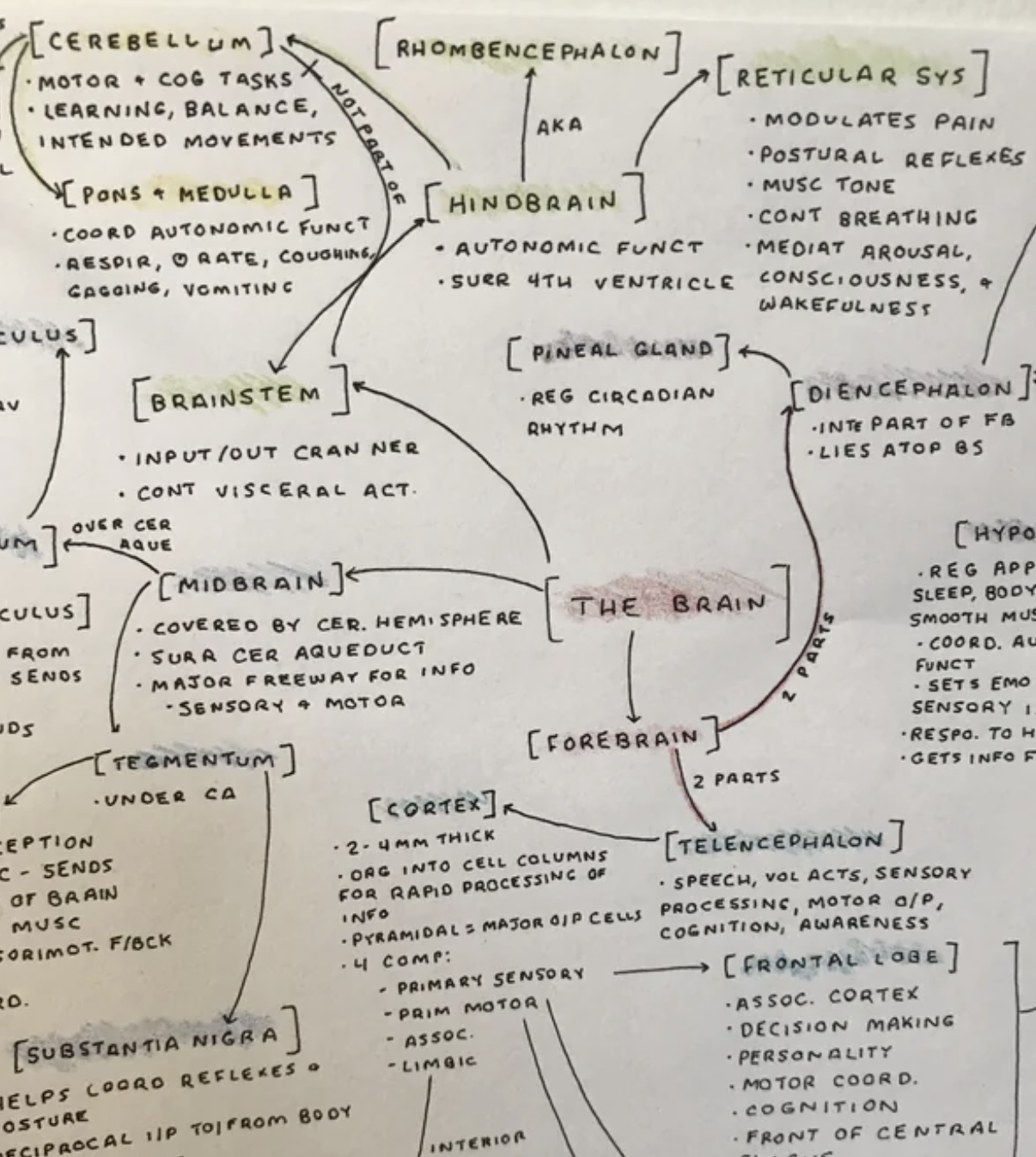
4.1. Why Mind Maps Are Especially Useful for Neuroanatomy
Mind maps provide a clear and concise visual representation of the relationships between different structures and systems in neuroanatomy. They can help you see the "big picture" and make connections between various topics.
4.2. Creating Mind Maps: Tips and Techniques
Start with a central concept (e.g., the brain) and branch out to related subtopics (e.g., cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem). Use colors, symbols, and images to differentiate between structures and functions. Connect related concepts to emphasize their relationships.
4.3. Examples of Neuroanatomy Mind Maps
Several resources offer pre-made neuroanatomy mind maps, or you can create your own using mind-mapping software or traditional pen and paper. Explore different formats and styles to find what works best for your learning preferences.
5. Recommended Resources for Learning Neuroanatomy
5.1. Best Free Online YouTube Channels
The following YouTube channels offer high-quality, accessible neuroanatomy lessons:
5.1.1. Kenhub
Kenhub provides a comprehensive library of videos, quizzes, and articles on various topics in anatomy, including neuroanatomy.

5.1.2. Dr. Najeeb Lectures
Dr. Najeeb offers detailed, easy-to-understand lectures on neuroanatomy and other medical subjects, with hand-drawn illustrations to aid visual learners.
5.1.3. Ninja Nerd Science
Ninja Nerd Science features in-depth video lectures on various medical topics, including neuroanatomy, with engaging visuals and clear explanations.
5.1.4. Handwritten Tutorials
Handwritten Tutorials offers concise, illustrated video tutorials on neuroanatomy and other medical subjects, with a focus on simplifying complex concepts.
5.2. Top Free Online Resources
The following websites provide free, high-quality neuroanatomy resources:
5.2.1. Neuroanatomy Online (University of Texas)
This comprehensive resource offers tutorials, quizzes, and interactive modules for learning neuroanatomy.

5.2.2. BrainFacts.org
Sponsored by the Society for Neuroscience, BrainFacts.org provides articles, videos, and interactive features on a wide range of neuroanatomy topics.
5.2.3. BrainMaps.org
BrainMaps.org offers high-resolution brain images, interactive tools, and informative articles to aid in neuroanatomy learning.
5.3. Best Books for Beginners
The following books are highly recommended for beginners learning neuroanatomy:
5.3.1. Neuroanatomy Made Ridiculously Simple by Stephen Goldberg
This concise and easy-to-understand book simplifies complex neuroanatomy concepts with the use of humor, mnemonics, and clear illustrations.
5.3.2. High-Yield Neuroanatomy by Douglas J. Gould and Jennifer K. Brueckner-Collins
High-Yield Neuroanatomy offers a focused approach to learning neuroanatomy, emphasizing essential information, clinical correlations, and board-style review questions.
5.3.3. Clinical Neuroanatomy Made Ridiculously Simple by Stephen Goldberg
Another excellent resource by Stephen Goldberg, this book focuses on the clinical aspects of neuroanatomy, providing essential information in a clear and concise manner.
5.3.4. Gray's Anatomy for Students by Richard L. Drake, A. Wayne Vogl, and Adam W. M. Mitchell
While not specifically focused on neuroanatomy, Gray's Anatomy for Students is a comprehensive anatomy textbook that covers neuroanatomy in depth, with detailed illustrations and clinical correlations.
6. Setting and Achieving Your End Goal
To succeed in mastering neuroanatomy and retaining the information long-term, follow these steps:
6.1. Defining Your End Goal as a Medical Student
Identify your specific objectives for learning neuroanatomy, such as preparing for exams, understanding clinical cases, or building a foundation for future studies.
6.2. Creating a Study Plan
Develop a personalized study plan that outlines the sequence of topics, study techniques, and resources you will use. Allocate sufficient time for each topic and schedule regular review sessions.
6.3. Tracking Your Progress and Adapting Your Study Methods
Monitor your progress by setting milestones and regularly testing your knowledge. Adapt your study techniques and resources as needed to address any areas of difficulty or confusion.
6.4. Preparing for Exams and Practical Assessments
Incorporate exam preparation into your study plan, including practice tests, quizzes, and hands-on activities, to ensure you are well-prepared for assessments.
6.5. Retaining Information for Long-term Memory
Reinforce your learning through spaced repetition, active learning, and engaging with the material in various formats (e.g., reading, videos, discussions, etc.).
Conclusion
Mastering neuroanatomy can be challenging, but with the right approach, study techniques, and resources, you can build a solid foundation and achieve your goals as a medical student. By following the guidance provided in this article, you will not only understand the material but also retain it for future application in your medical career. Embrace the learning process and remember that a strong foundation in neuroanatomy will serve you well throughout your medical journey.