The Birth of Synthetic Life: A Leap Forward for Medical Research
In the realm of science fiction, cloning often forms a central theme. From Star Wars to the philosophical works of Philip K. Dick, human cloning has been depicted in various ways. Yet, the real-world exploration of these concepts takes us far beyond the realm of fiction into an extraordinary field of medical research.
In a groundbreaking scientific achievement, researchers have made strides in the development of synthetic embryos – entities that could one day revolutionize organ transplantation and drug testing, while simultaneously raising a plethora of ethical questions.
For decades, the creation of an artificial clone, be it a complex organism or a simple cellular construct, seemed an unattainable dream. But with recent advances, scientists are beginning to understand how embryos grow, hinting at a future where artificial embryonic constructs become a reality.
“They were two babies, they were grown in conditions outside of the human body and usually cloned from a single cell...”
Initially, the focus has been on creating synthetic mice embryos. This may seem far removed from the grand vision of cloning a human being, but the applications for medical research are staggering. The organoid – a simplified, miniaturized organ grown in vitro – already serves as a powerful tool for studying the effects of drugs and various diseases, contributing to a reduction in the use of animal testing. However, the synthetic embryo would go a step further, offering a more complex construct for rigorous scientific scrutiny.
“When it comes to, for example, biological printing or the idea of making organs using 3D bioprinter, there is a limitation today...”
The production of these synthetic embryos, as with organoids, begins with a single stem cell, not derived from any sexual interaction, but from the body of a mouse. These stem cells can differentiate into a myriad of other cells, such as skin cells or brain cells, and therefore present an incredible potential for experimentation.
The process used to create these synthetic embryos, though, is much more complicated than the straightforward growth of organoids. The experiment began with growing three separate types of cells in a simulated environment, then placing these cells into an artificial womb where they could interact and self-organize into an early embryo-like structure.
Making of a Synthetic Embryo: A Groundbreaking Feat
It's fascinating how a single stem cell, not a sperm cell, not a cell that involved any kind of sexual activity, has been turned into a synthetic embryo that couldn't develop into anything complex afterwards. How was this achieved?
Scientists started by using a fertilized cell, developing an artificial womb to facilitate the growth of these cells into a tiny embryo. This was an astounding breakthrough as none of these embryos had ever survived in petri dishes before.
This artificial womb mimicked the conditions inside the uterus, including the rotation simulating the blood and nutrient flow in the placenta, and replicating the atmospheric pressure. A remarkable invention of 2021, this device is now facilitating studies using stem cells.
"In some sense the scientist here created what you would call an artificial womb or a kind of an external uterus that could be then used to grow more embryos."
The breakthrough moment came when these synthetic embryos, through their unique environment and combination of chemical signals and mechanical interactions, developed a beating heart and a rudimentary brain, an unprecedented achievement in this line of research.
Despite these astonishing developments, a significant point to note is that these synthetic embryos, while closely resembling the real thing, cannot actually develop into living creatures. This is a crucial aspect to consider when evaluating the ethical implications of such research, as the inability to develop into a living being delineates synthetic embryos from their natural counterparts.
“...these synthetic embryos, at least statically, could not really be seen as a living being...”
The scientists had not only created a synthetic embryo, but they also discovered the vital role of mechanical interaction in organ development. The early cells received not only chemical signals but also experienced essential mechanical interaction, usually through touch, to develop into an organ.
The application of these synthetic embryos is potentially transformative. Not only could they be used for more complex drug testing and medical studies, but they might also help us understand why certain embryos fail during pregnancy, a topic of significant concern. This knowledge could improve the success rate of pregnancies, reducing the risk of failed pregnancies that can, tragically, also result in maternal death during childbirth.
Additionally, the concept of synthetic embryos holds promise for organ transplantation. Rather than waiting for a suitable donor, organs could potentially be grown from these synthetic embryos, solving the issue of donor shortages and reducing the risk of organ rejection.
“This new development could mark a turning point in how we approach organ transplantation...”
Ethics, the Implications and the Future
This breakthrough is not without its ethical considerations. Critics argue that creating synthetic embryos, even with their current limitations, steps perilously close to the creation of life, prompting necessary discussions about the moral implications of this research.
At what point, they ask, does a clump of cells become an individual being with rights? When does it become morally unacceptable to create or destroy these synthetic entities? As we push the boundaries of what we can accomplish in the lab, it is essential to continually reevaluate the ethical guidelines that govern our work.
The creation of a synthetic mouse embryo represents a quantum leap in the field of medical science, with implications that reach far beyond the confines of a laboratory. By studying and experimenting with these synthetic constructs, we edge closer to a future where organ transplantation becomes less risky, drug testing becomes more accurate, and the mysteries of embryonic development are unravelled.
Yet, as we charge into the future, we must also remain cognizant of the ethical conundrums that our progress may create. The balance between scientific discovery and ethical considerations is a delicate one, and as we venture further into the realm of synthetic life, it is a balance that we must continually strive to maintain.
“...ethics and morals should guide our scientific endeavors as we tread into uncharted territories...”
From cloning to synthetic embryos, the scientific community continues to break barriers, revealing new facets of life and its potential for manipulation. Although these advancements are still in their early stages, the trajectory of this research is undoubtedly transformative, heralding a new era in medical science and forcing us to confront the realities – and responsibilities – of wielding such formidable power.
What once was merely a concept relegated to the realm of science fiction, synthetic life is rapidly becoming a scientific reality. The synthetic embryo is a harbinger of new possibilities, bringing us one step closer to understanding life's complex tapestry. As we navigate this brave new world, we must be mindful of the enormous ethical challenges that accompany these groundbreaking advances, reminding ourselves that progress, while exciting, also carries profound responsibility.
Nature magazine article
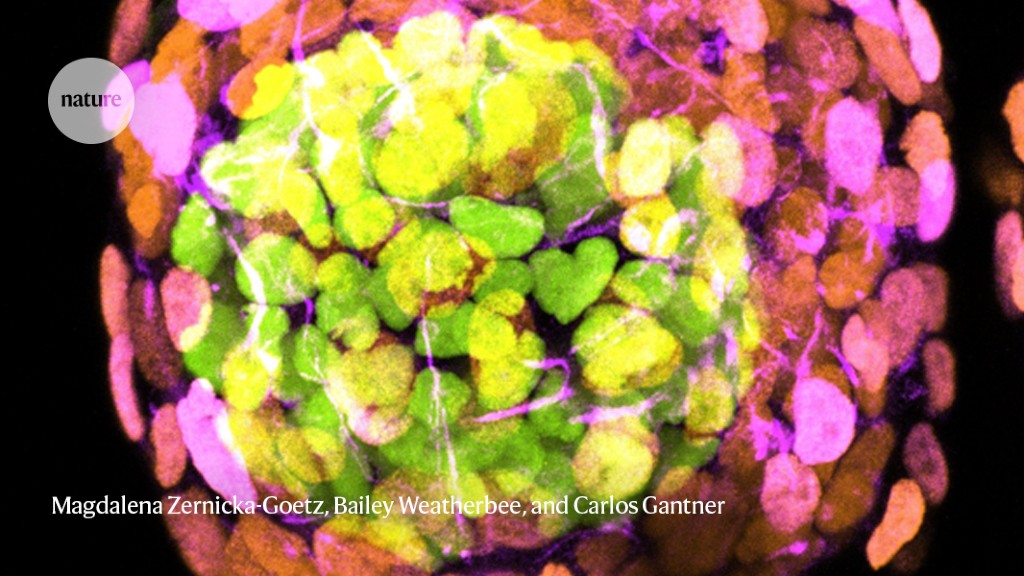
In conclusion, what once was merely a concept relegated to the realm of science fiction, synthetic life is rapidly becoming a scientific reality. The synthetic embryo is a harbinger of new possibilities, bringing us one step closer to understanding life's complex tapestry. As we navigate this brave new world, we must be mindful of the enormous ethical challenges that accompany these groundbreaking advances, reminding ourselves that progress, while exciting, also carries profound responsibility.