Ah, the age-old debate: studying medicine in the United States or Europe? It's a question that has plagued many aspiring doctors for years, as they weigh the pros and cons of pursuing their dreams on either side of the Atlantic. With different educational systems, cultural experiences, and opportunities awaiting in each corner, the decision is anything but easy. But fear not, future healers! We've got your back. In this article, we'll delve into the nitty-gritty of what it's like to study medicine in the US and Europe, so you can make an informed decision about which path to choose.
Whether you're a premed student with stars in your eyes, a medical student knee-deep in textbooks, or a newly minted doctor seeking the best opportunities, we've got something for everyone. So grab your stethoscope, put on your thinking cap, and let's embark on this whirlwind tour of medical education on both sides of the pond!
Below is a table comparing some key aspects of medical schools in the European Union (EU) and the United States (US). Please note that this comparison is meant to provide an overall understanding, and individual schools within each region may differ in specific policies and requirements.
| Category | EU Medical Schools | US Medical Schools |
|---|---|---|
| Length of Program | Typically 6 years (direct entry from high school) | 4 years (after completing a 4-year undergraduate degree) |
| Admission Requirements | High school diploma, entrance exams, language proficiency | Bachelor's degree, MCAT, prerequisite courses, extracurriculars |
| Curriculum | Integrated approach: basic sciences and clinical training | 2 years basic sciences, 2 years clinical rotations |
| Tuition Fees | Generally lower than US schools, varies by country and school | Typically higher, varies by school (public vs private) |
| Language of Instruction | Varies; English-taught programs available in some countries | English |
| International Recognition | Varies; ECFMG certification required to practice in the US | Widely recognized; easier access to US residency programs |
| Clinical Training | May be conducted at hospitals affiliated with the university | Affiliated teaching hospitals and clinical sites |
| Residency | Varies by country; may be called "specialty training" | 3-7 years (depending on specialty) post-graduate |
| Licensing | National licensing exams and requirements in the country of study | USMLE Step 1, Step 2 CK and CS, and Step 3 for US licensing |
| Research Opportunities | Varies by institution, generally less emphasis on research | Abundant research opportunities, highly encouraged |
US: Bachelor's degree and prerequisite courses
In the United States, the road to becoming a doctor often begins with a four-year undergraduate degree. As a premed, you can major in virtually any field, as long as you complete the prerequisite courses required for medical school admission. These typically include biology, chemistry, organic chemistry, physics, and sometimes biochemistry and calculus. While this flexibility allows you to explore your interests beyond medicine, it also means you'll spend more time in school before getting to the real medical action.
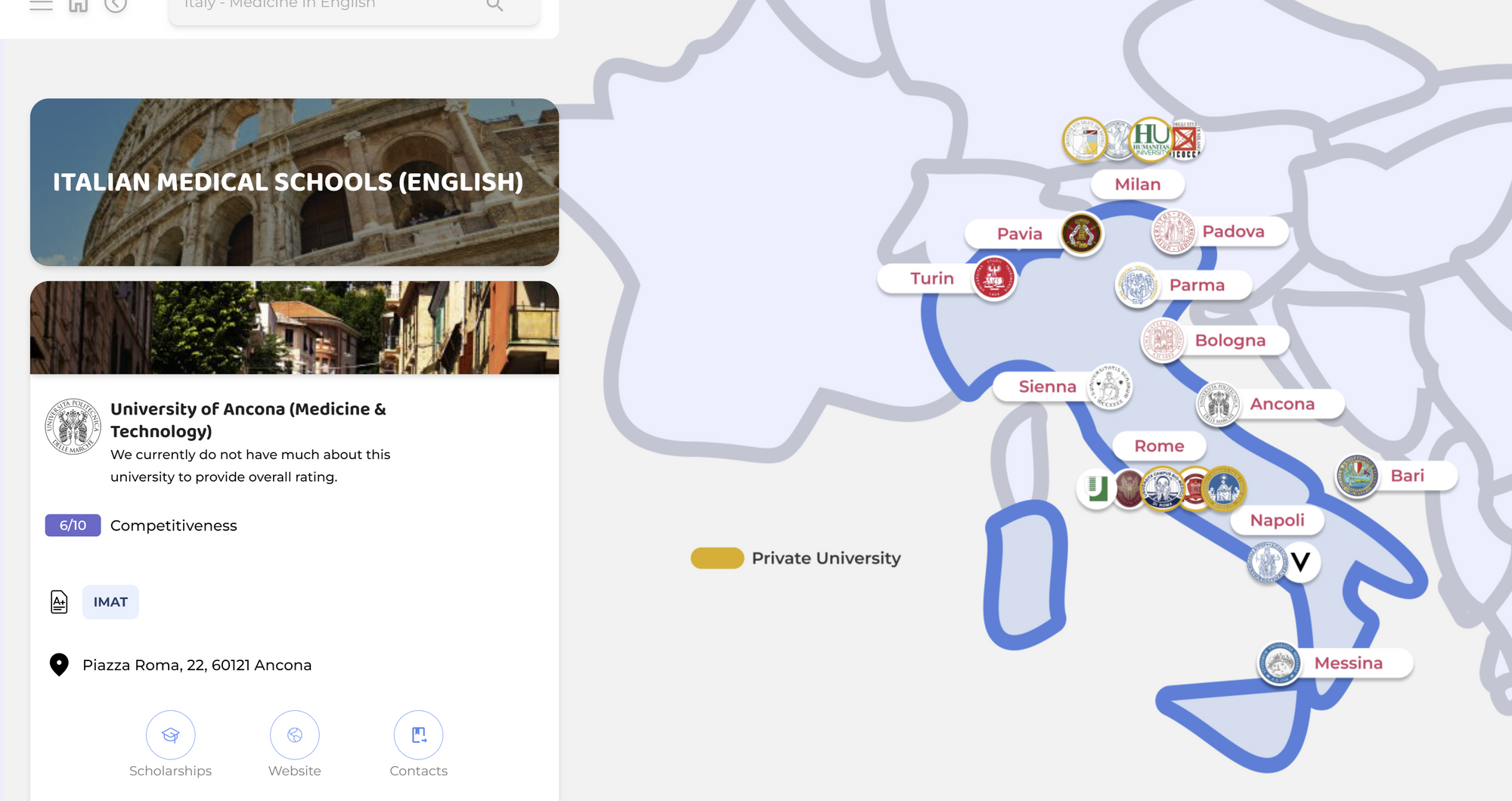
Europe: Direct entry into medical programs
On the other side of the Atlantic, European countries tend to offer direct entry into medical programs, typically right after high school. This means you'll dive headfirst into the world of medicine, without the need for a separate bachelor's degree. You'll spend more time focusing on your chosen field, and you'll likely graduate sooner than your American counterparts. However, this early specialization can make it harder to switch careers if you have a change of heart down the line.
Application process and entrance exams
The application process for medical schools can be quite different between the US and Europe. In the US, you'll need to take the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) and submit a comprehensive application through a centralized system (AMCAS, AACOMAS, or TMDSAS), which includes your personal statement, letters of recommendation, and a record of your extracurricular activities. Competition can be fierce, so standing out from the crowd is essential.
European medical schools often require entrance exams, which may be country-specific, like the UK's UCAT and BMAT, or specific to individual schools. Language proficiency tests may also be required for non-native speakers. The application process can vary widely from country to country, so it's crucial to do your homework and prepare for each school's unique requirements.
Medical School Structure and Duration
4-year MD program
In the US, medical school typically lasts four years and leads to a Doctor of Medicine (MD) degree. The first two years mainly focus on basic sciences, such as anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology, with some early clinical exposure through simulated patient encounters and observations. The last two years consist of clinical rotations in various specialties, where students gain hands-on experience working alongside doctors and residents.
Europe: 5-6 year programs
European medical schools generally offer 5-6 year programs, often leading to degrees like the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) or its equivalent. The structure can vary by country, but most programs integrate theoretical knowledge and clinical practice throughout the curriculum. This means you'll start building your clinical skills earlier than in the US, giving you more time to hone your abilities in real-life settings.
Comparing teaching styles and clinical experience
Teaching styles and methods can differ significantly between the US and Europe. American medical schools often employ a combination of lectures, small group discussions, problem-based learning, and simulations. In Europe, traditional lectures may be more common, but innovative teaching methods are becoming increasingly popular, including case-based learning and team-based learning.
When it comes to clinical experience, both US and European medical students have opportunities to work in various healthcare settings and specialties. However, the degree of responsibility and autonomy given to students may differ, with some European countries offering more hands-on experience earlier in the curriculum.
Ultimately, the choice between studying medicine in the US or Europe will depend on your preferred learning style and the level of clinical involvement you're seeking during your education.
Postgraduate Training and Residency
US: Competitive residency matching process
After completing medical school in the US, graduates must enter a residency program in their chosen specialty. The matching process is highly competitive and involves submitting an application through the Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS) and interviewing with residency programs. The National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) then uses an algorithm to match applicants with programs based on both parties' preferences.
Europe: Various pathways and specialization options
In Europe, the path to postgraduate training can vary widely depending on the country. Generally, after graduating from medical school, European doctors enter a specialization program, which can range from 3 to 7 years, depending on the field. The application process, selection criteria, and availability of positions differ from country to country, so it's important to research each nation's specific requirements.
Duration and work-life balance during training
Residency training can be demanding in both the US and Europe, with long hours and high expectations. However, there are some differences in terms of work-life balance. In the US, strict regulations limit residents' work hours to 80 hours per week, while European countries have adopted the European Working Time Directive, which limits work hours to 48 hours per week on average. This can translate to a better work-life balance for European trainees, although the actual experience may vary depending on the program and specialty.
Costs and Financial Considerations
Tuition and fees in the US
One of the most significant factors to consider when choosing between studying medicine in the US and Europe is the cost. Medical education in the US is notoriously expensive, with tuition and fees at public and private schools often exceeding $50,000 per year. This can result in substantial debt for medical students, which may take years to repay.
Affordable education in Europe
In contrast, many European countries offer affordable or even free medical education to their citizens and, in some cases, international students. Tuition fees vary, but are generally much lower than in the US, making medical education more accessible and less financially burdensome.
Scholarships and financial aid opportunities
Both the US and Europe offer various scholarships and financial aid opportunities for medical students. In the US, options include federal and private loans, scholarships, and grants, while European countries may provide government-sponsored scholarships, stipends, and low-interest loans. It's crucial to research and apply for financial aid opportunities early in the application process to minimize the financial burden of medical education.
International Opportunities and Exchange Programs
Study abroad and research experiences
One of the exciting aspects of studying medicine is the opportunity to broaden your horizons through international experiences. Both US and European medical schools often offer study abroad and exchange programs, allowing students to gain exposure to different healthcare systems, cultures, and practices. These experiences can be incredibly enriching, both personally and professionally, and help foster a global perspective on healthcare.
Collaboration between US and European medical schools
There is a growing trend of collaboration between US and European medical schools, which can provide students with unique educational experiences and networking opportunities. Joint research projects, dual degree programs, and shared educational resources are just a few examples of how medical schools on both sides of the Atlantic are working together to enhance the training of future physicians.
Impact on career prospects
International experiences, such as studying or working abroad, can have a positive impact on your career prospects. Having a diverse background and understanding of different healthcare systems can make you an attractive candidate for positions in academia, research, global health, or multinational healthcare organizations. Additionally, building connections with medical professionals around the world can open doors to new opportunities and collaborations.
Cultural and Lifestyle Differences
Adjusting to a new country and culture
Choosing to study medicine in a different country comes with its own set of challenges and rewards. Adapting to a new culture, language, and way of life can be both exhilarating and daunting. Embracing these differences and immersing yourself in the local culture can enrich your personal growth and help you develop a more inclusive and empathetic approach to patient care.
Work-life balance and personal growth
Work-life balance is an important consideration for medical students and professionals alike. While both US and European medical schools require dedication and hard work, cultural differences in attitudes towards work, leisure, and personal time can impact your overall experience. Exploring these differences and finding a balance that suits your needs can contribute to a more fulfilling and sustainable medical career.
Networking and making connections in a global community
Studying medicine in the US or Europe provides ample opportunities to network and make connections within the global medical community. Attending conferences, participating in research projects, and joining professional organizations can help you expand your network and establish relationships with like-minded professionals. These connections can lead to future collaborations, job opportunities, and personal growth.
Employment and Post-Graduation Opportunities
Job market and earning potential
The job market for physicians is generally favorable in both the US and Europe. However, earning potential can differ significantly between countries. US doctors tend to earn higher salaries than their European counterparts, but the cost of living, taxes, and student loan repayment can impact your overall financial situation.
Licensing and board certification
After completing medical school and postgraduate training, doctors must obtain licensure and, in some cases, board certification in their specialty. The process for obtaining these credentials varies between the US and European countries, and often involves passing exams and fulfilling additional training requirements. It's essential to familiarize yourself with the specific requirements for the country where you plan to practice.
Opportunities for research, academia, and innovation
Both the US and Europe offer abundant opportunities for physicians interested in research, academia, or innovation. Leading research institutions, prestigious universities, and cutting-edge technology companies can be found on both sides of the Atlantic, providing ample options for those looking to contribute to the advancement of medicine and healthcare.
Conclusion
Weighing the pros and cons
Deciding where to study medicine is a deeply personal choice that depends on numerous factors, including your educational goals, preferred learning style, financial situation, and long-term career aspirations. It's essential to weigh the pros and cons of studying medicine in the US and Europe to determine the best fit for your individual needs.
Personal preferences and long-term goals
Consider the structure and duration of the programs, the teaching styles, the level of clinical experience, and the postgraduate opportunities in each region. Additionally, think about your personal preferences, such as the lifestyle and cultural aspects of living in a different country, and how they align with your long-term goals.
Making an informed decision for a rewarding medical career
Ultimately, the choice between studying medicine in the US and Europe should be based on an informed understanding of the similarities and differences in both systems. By carefully considering your options and assessing your priorities, you can embark on a fulfilling and rewarding medical career, whether it's on the bustling streets of New York City, the historic halls of a European university, or anywhere in between.