Hi there! My name is Ari Horesh, and as a medical student who has tutored hundreds of students every year for different admission exams, I've been asked countless times to create a list of the best study techniques for medical students. After years of trial and error, I'm excited to share my ultimate guide for studying smarter, not harder. This guide will serve as an introduction to the world of study techniques, covering the basics before diving into more advanced techniques. Whether you're a medical student or about to take the admission exam this guide is designed to help you study more effectively and efficiently. We'll cover a range of basic topics, from creating a study schedule to using online resources and everything in between. By the end of this article, you'll have a good understanding of both the wide world of study techniques and the basic terminology commonly used. So, let's dive in and get started!
Creating a Basic Study Schedule
Creating a study schedule is one of the most important things you can do to study smarter, not harder. It's crucial to start preparing from the beginning of the semester, dedicating at least 1-2 hours a day to studying. Waiting until the exam session to start studying can lead to cramming, which is not an effective way to learn and retain information.
To create a study schedule, start by looking at the course syllabus. Most courses in university and admission exams have a course syllabus that outlines the material that will be covered throughout the semester. This syllabus is a great starting point for creating a study schedule.
One tool that can be very helpful in creating a study schedule is ChatGPT. ChatGPT can help you create a study schedule based on your course, organize the material into sections, and set up a timeline for studying. This can take the guesswork out of creating a study schedule and help you stay on track.
It's also recommended to use a to-do list on a daily basis. You can schedule your to-do list ahead of time, so you always have the overall picture of what you should do right in front of you. Having a to-do list in front of you will allow you to visually grasp your progress, which is known to help you stay motivated and consistent.
By creating a study schedule and to-do list, you'll be able to break down the material into manageable chunks and set realistic goals for yourself. This will help you stay on track and avoid feeling overwhelmed. So, take some time to create a study schedule and to-do list, and you'll be on your way to studying smarter, not harder.
Things To Consdier And Add To Your Shcedule
One of the most effective ways to study smarter, not harder, is to prioritize high-yield topics. High-yield topics are those that are most likely to appear on exams and are essential for your future medical career. Here are some tips for prioritizing high-yield topics:
- Identify high-yield topics: As mentioned earlier, you can identify high-yield topics by looking at the course syllabus, previous exams, and textbooks. Focus your efforts on these topics and make sure you understand them thoroughly.
- Make use of study guides: Study guides, such as review books and flashcards, can be a great way to identify high-yield topics and reinforce your knowledge. You can get them online but most of the time you will be able to get them from upper year students who already summaries and studied these topics.
- Utilize active learning techniques: Active learning techniques, such as quizzing yourself or teaching the material to someone else, can help you retain information better and identify areas where you need to focus your studying efforts. While we will review these study techniques later on, it is important to mention that quizzing yourself and teaching the material/discussing it with your classmates is something you should definetely add to your schedule.
Adding Breaks To Your Schedule
Practicing good study habits is an essential part of studying smarter, not harder. While it's easy to add only the things you need to study to your schedule, it's important to include other activities that are important for your overall health and well-being. Here are some tips for incorporating good study habits into your schedule:
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is important for staying hydrated and keeping your brain functioning properly. Make sure to schedule regular water breaks throughout your study sessions.
- Get enough sleep: Getting enough sleep is crucial for your overall health and well-being, as well as your ability to learn and retain information. Aim for at least 8 hours of sleep each night and make sure to include a consistent sleep schedule in your study plan.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise is important for both your physical and mental health. Schedule time for exercise in your study plan, whether it's a morning workout or an evening yoga class.
- Eat a healthy diet: A healthy diet is essential for staying focused and energized during your study sessions. Plan healthy meals and snacks in advance to avoid relying on unhealthy food options during stressful times.
- Take breaks for rest and relaxation: It's important to take regular breaks for rest and relaxation to avoid burnout and stay productive. Schedule breaks for activities such as reading, listening to music, or simply taking a nap.
Incorporating these good study habits into your schedule can help you stay productive and keep you going in the long run. Remember, studying smarter, not harder, is not just about studying more, but also about taking care of your body and mind. So, make sure to include these good study habits in your schedule and prioritize your overall health and well-being.
Active Learning Techniques In Medical School
Active learning techniques are essential when you are intrested in studying smarter. These techniques involve engaging with the material in a way that promotes deeper learning and understanding. Here are some of the most effective active learning techniques to consider incorporating into your study routine:
Active Recall and Spaced Repetition
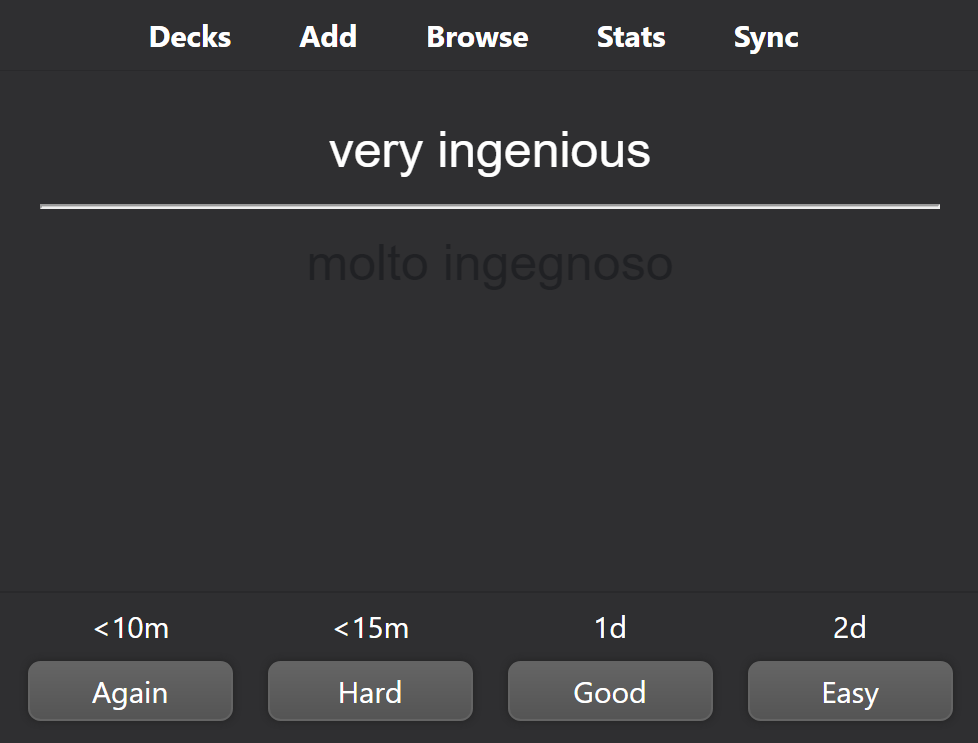
Spaced repetition is a powerful technique that has been proven to help students learn and retain information more effectively. The technique involves reviewing material at increasing intervals of time, with the goal of reinforcing your memory and increasing your retention of the material. But what is the neurological mechanism behind spaced repetition, and why does it work so well?
At the heart of the spaced repetition technique is the idea of active recall. When you actively recall information, you are essentially practicing retrieving that information from memory, rather than simply reading or re-reading it. This process of active recall is important because it helps to reinforce your memory of the material and increase your retention of the information.
But how does the brain actually retain information over time? It turns out that the process of learning and memory involves changes in the strength and connectivity of synapses, the tiny gaps between neurons in the brain. When you learn something new, your brain forms new synapses or strengthens existing ones, which allows the information to be stored more effectively.
However, these changes in synapse strength are not permanent. Over time, if the information is not used or reinforced, the synapses can weaken or even disappear, leading to forgetting. This is where spaced repetition comes in. By reviewing the material at increasing intervals, you are essentially strengthening the synapses in your brain and making it more likely that the information will be retained over the long term.
The neurological mechanism behind spaced repetition is complex, but the basic idea is that by actively recalling information at increasing intervals, you are strengthening the connections between neurons in your brain and increasing your retention of the material. By incorporating spaced repetition into your study routine, you can learn and retain information more effectively, and ultimately study smarter, not harder! So, why not give it a try and see how it works for you?
The Pomodoro Technique
The Pomodoro Technique is a time management strategy that has gained popularity among professionals, students, and individuals seeking to increase their productivity. This technique involves breaking down work into short, focused intervals, typically 25 minutes, followed by a brief break. The Pomodoro Technique is based on the idea that working in short, concentrated bursts can improve focus, increase productivity, and reduce mental fatigue.
Neurologically, the Pomodoro Technique works by capitalizing on the brain's natural rhythms. The brain is wired to work in cycles of focused attention and rest. These cycles are governed by the brain's default mode network, which is responsible for regulating the brain's attention and focus. By breaking work into short, focused intervals, the Pomodoro Technique harnesses the brain's natural ability to maintain focus for short periods and then reset. This process not only boosts productivity, but it also reduces mental fatigue and increases motivation.
The Pomodoro Technique also incorporates several psychological concepts. The first concept is that of time management. By setting a specific time for work and breaks, individuals are forced to prioritize their tasks and work more efficiently. This helps to prevent procrastination and encourages individuals to stay on task. Additionally, the Pomodoro Technique utilizes the concept of goal-setting. By breaking work into manageable intervals, individuals can set specific goals for each interval, which helps to increase motivation and focus.
Another psychological concept involved in the Pomodoro Technique is that of habit formation. By consistently using the Pomodoro Technique, individuals can develop a habit of working in short, focused bursts, which can lead to long-term improvements in productivity and focus. Finally, the Pomodoro Technique incorporates the concept of self-awareness. By tracking work intervals and breaks, individuals can gain insight into their own productivity and adjust their work habits accordingly.
There is a wealth of evidence to support the benefits of the Pomodoro Technique. Studies have shown that the Pomodoro Technique can improve productivity, reduce mental fatigue, and increase motivation. Additionally, the Pomodoro Technique has been shown to be effective in improving time management skills and reducing procrastination. By capitalizing on the brain's natural rhythms and incorporating key psychological concepts, the Pomodoro Technique is a powerful tool for anyone seeking to boost their productivity and focus.
Feynman Technique
The Feynman Technique, named after the Nobel Prize-winning physicist Richard Feynman, is a popular learning strategy that involves explaining complex concepts to a friend as if they had no prior knowledge of the topic. This technique not only helps simplify difficult ideas, but it also has additional benefits when you involve a study buddy.
When you have a study buddy, it increases accountability, making it more likely that you will show up for study sessions and put in more effort. Additionally, studying with a friend can enhance your learning experience by providing opportunities for discussion and asking questions. This leads to increased cues associated with the memory formed, as the act of answering a friend's questions and engaging in conversation helps reinforce the information in your mind.
By involving a friend in your studying, you can also improve your metacognitive and self-regulated learning skills, which involve managing your own learning process. Collaborating with a friend can also help reduce cognitive load, which is the amount of mental effort required to process information. As a result, the Feynman Technique with a study buddy can increase motivation, reduce stress, and enhance the learning experience.
In summary, the Feynman Technique is an effective learning strategy that involves explaining complex concepts to a friend. When you add a study buddy to the mix, you can increase accountability, reinforce information through discussion, and improve metacognitive and self-regulated learning skills. The benefits of having a study buddy include improved motivation, reduced stress, and a more enjoyable learning experience.
The Leitner System
The Leitner System is a popular and effective study technique used by many students to improve their retention of information. The system was developed by German psychologist Sebastian Leitner in the 1970s and is based on the principle of spaced repetition. Here's a guide for students on how to use the Leitner System:
- Gather your study materials: The Leitner System is best used for studying facts or information that can be broken down into discrete pieces. For example, vocabulary words, math formulas, historical dates, or chemical elements.
- Create flashcards: Write each fact on one side of a flashcard and the corresponding answer or definition on the other side. You can use physical flashcards or digital flashcards using an app like Quizlet or Anki.
- Divide the flashcards into boxes: You'll need at least three boxes or compartments for this system to work. Label each box with a number or a name that indicates how frequently you'll be reviewing the cards in that box.
- Start with Box 1: Place all the flashcards in Box 1 to start. Review each flashcard and test yourself on the information. If you get the answer correct, move the flashcard to Box 2. If you get it wrong, return the card to Box 1.
- Move cards between boxes: Each time you review the flashcards, move the ones you get correct to the next box. The more times you successfully recall the information on a flashcard, the longer you wait until the next review. For example, Box 2 might be reviewed every day, Box 3 might be reviewed every three days, and Box 4 might be reviewed once a week.
- Review regularly: Make a habit of reviewing your flashcards on a regular schedule. This will help you maintain your knowledge and avoid forgetting the information you've learned.
- Monitor your progress: Keep track of how many flashcards are in each box and how frequently you're reviewing them. Adjust your study schedule as needed to ensure you're retaining the information effectively.
Hey! Can you summaries the article for me and format it in a bullet point list? Thank you!
Summary
- The article provides a guide for studying smarter, not harder for medical students.
- Creating a study schedule is essential for effective studying, with dedicating at least 1-2 hours a day to studying.
- To-do lists can be helpful in visualizing progress and setting realistic goals.
- Prioritizing high-yield topics, identifying them through the course syllabus and using study guides can be effective.
- Incorporating good study habits such as staying hydrated, getting enough sleep, exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, and taking breaks for rest and relaxation is important for long-term productivity.
- Active learning techniques, such as active recall and spaced repetition, the Pomodoro technique, the Feynman technique, and the Leitner system, can enhance learning and retention of information.
- The Pomodoro technique is a time management strategy that breaks work into short, focused intervals followed by brief breaks to improve productivity and reduce mental fatigue.
- The Feynman technique involves explaining complex concepts to a friend, and the Leitner system is a study technique that uses flashcards and spaced repetition to improve retention of information.